Is Endgame an environmental movie about our greatest fears?

Avengers: Endgame is generally not often talked about as an environmental movie that explores our greatest fears about the damage we have inflicted onto this planet. But that’s exactly what it is, writes Danielle Clode from Flinders University.
I had a momentary brain-fade when I went to the movies this week.
“Three tickets to … what’s it called again?” I asked.
“Endgame”, the ticket seller replied firmly, “What other movie is there?”
At over three hours long, it certainly is a movie for the fans, packed full of emotionally satisfying vignettes and snappy interactions for the cast of thousands that has become the Avengers trademark. I don’t think I’ve ever watched a faster three-hour movie.
Avengers: Endgame, the concluding half of Avengers: Infinity War, has quickly become one of the biggest grossing movies of all time. By pure numbers these are important and influential movies. So what are they are telling us?
Let me say at the outset that this is not a critique of the movie itself. I’m not going to document plot holes, flaws in logic or whether or not the science is correct. I’m happy to suspend a bit of disbelief for the sake of a good story. But I am interested in the function that stories like these play and what they reveal about our broader hopes and fears.
Although not pitched as one, Endgame is an environmental movie – and an apt one for our times. Its predecessor, Infinity War, saw the world under threat from powerful villain Thanos, whose home world had been destroyed by overpopulation and resource exploitation. His grief sets him on a quest (involving, naturally, a gauntlet studded with variously magical and powerful stones) to halve the population of the universe.
Despite being cast as the antagonist, it is Thanos’s character who undertakes the “hero’s journey” in this movie. By the end of Infinity War, Thanos manages to achieve his goal across the universe, without violence – painlessly and humanely, with a click of the fingers – wiping out exactly 50% of the population at random, all at once.
It’s a little unclear in Infinity War what Thanos intends to reduce: half the human population or half of all sentient life. His track record had focussed on people, killing “people planet by planet, massacre by massacre”. In Endgame the goal is broadened. Not just all humans or even all sentient life forms, not just the resource exploiters and over-users, but half of all life forms. It’s a telling ecological misstep.
Clearly, it’s the people that matter and humans in particular. Despite having the breadth of the universe as a stage, even the alien Avengers are strikingly Earth-centric, with the exception of Captain Marvel/Carol Danvers, who is the only one, aside from Thanos, who cares that the same thing is happening across thousands of planets.
Various critics have discussed whether Thanos’s population reduction strategy would work – at least in terms of halving the human population of Earth. And they generally conclude that it wouldn’t.
But this is an over-simplification of the movie’s message. The specific population reduction strategy Thanos employs can also be read as a broader environmental goal – to “restore” ecological balance. Climate change, pollution, species extinctions, overpopulation, resource use and distribution are all connected parts of the broader issue of environmental sustainability. The question is not, is population reduction a viable strategy? (Probably not.) Nor even, would a reduced human population be good for the planet? (Perhaps, if it were sustainable.)
The question Endgame poses for us is, are we willing to make personal sacrifices to save our own futures? To which the answer is a categorical no.
Our greatest fears
Eco-catastrophe fiction is often castigated for not being scientifically accurate, and for failing to promote action on any of the various threats that face our planet – overpopulation, pollution, extinction, nuclear fallout, climate change. But when my colleague and I looked at climate change fiction across the centuries, we found that such stories are not about providing answers to our problems, but articulating our greatest fears. These stories – in book or movie form – are reflections of how society imagines the world of the future.
Eco-catastrophe stories have been a part of our culture from the earliest mythological stories of floods, fires, eruptions and storms. These stories of punishment and redemption form the foundation for much of our literature, not least that of superheroes with god-like or even godly powers.
The emergence of both the novel (and modern science) in the 17th and 18th centuries saw a growing awareness of environmental change reflected in fiction. Early Romantic literature may have seen climate change as a metaphor for social progress and human advancement into a Utopia, but that rapidly shifted into the dystopian fears that dominate environmental fictional literature today.
From the mid-19th century onwards, fiction, and particularly science fiction, closely tracked developments in science. Our deeper understanding of past ice-ages and the influence of solar variation, geological instability and the oscillations of the earth on climate, emerged in stories like Gabriel De Tarde’s Underground Man, S Fowler Wright’s Deluge and William Wallace Cook’s Tales of Twenty Hundred.
Extra-terrestrial influences (comets rather than aliens) provided the catalyst for eco-catastrophe fiction in the 19th and 20th centuries. This phase was a phenomenon undoubtedly inspired by the first-hand experience of the “little Ice Age” which caused widespread famine, crop failures, and food riots across the Northern Hemisphere. Astronomer Camille Flammarion’s Omega: The Last Days of the World (1893-4) was perhaps one of the most influential of the comet-inspired fictions and marked the continuing dominance of dystopian over utopian visions for the future.
This pattern continued into the 20th and 21st centuries and, as the climate change debate expanded from a restricted scientific focus to a broader social and political dimension, the literature expanded from science fiction to a broader range of literary forms. Eco-catastrophe has emerged in every genre from thrillers to literary fiction and particularly young adult fiction. And of course, in the visual forms of storytelling – superhero, science fiction and apocalypse movies.
A sense of inevitability and hopelessness pervades much of the modern literature on climate change, irrespective of sub-genre. Rarely is climate change depicted as being solved by human agency. For many, the damage of climate change can only be overcome with the assistance of either supernatural or extra-terrestrial powers. We can see the same patterns in movies where the future of humanity is so often saved by superior intelligence rather than our own, either aliens, angels, or, as in Interstellar, our unrecognisably advanced selves.
Distrust of scientists
The history of eco-castastrophic stories reveals that, far from being agents of resolution and improvement, scientists are mostly depicted as untrustworthy or even responsible for the crisis. Environmentalists are even less trustworthy than the scientists; they are frequently depicted as extremist and violent loonies.
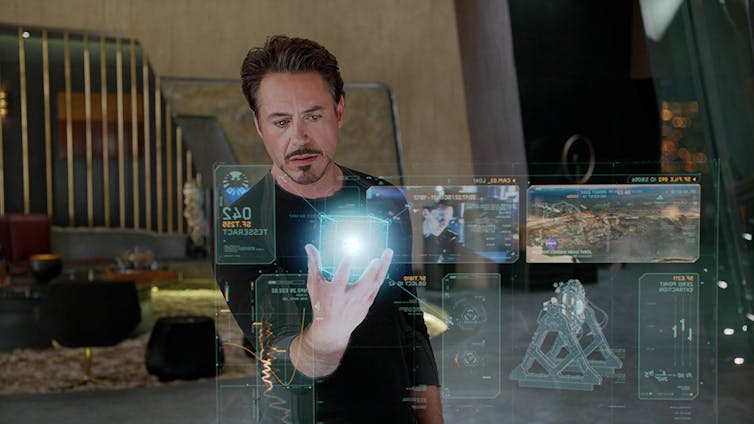
This distrust is reflected throughout the Avengers franchise. The original 2012 Avengers film saw Tony Stark’s (aka Iron Man) sustainable power source, the Arc Reactor, co-opted to create a wormhole entry point for alien invasion. The shadowy law enforcement agency, SHIELD, subverts research into the environmental potential of the Tesseract, an alien object with infinite energy, for weapons development. The same theme recurs – green technology is dangerous and scientists cannot be trusted.
And nor can “environmentalists” like Thanos. On his home planet, his environmental crusade earns him the title “The Mad Titan”. By the end of Infinity War, however, he has completed his quest, accepted the sacrifice his choices entail, and his hero’s journey is at an end. Both he and the world have been transformed into a new order. Thanos sits in the countryside and watches the sunset.
Except that it’s not a happy ending. Endgame opens with a powerful scene that illustrates the central problem. Clint Barton (or to use his “made-up name”, Hawkeye) is picnicking with his family in the country – having given up his action persona – and is teaching his daughter to shoot arrows. As he turns away for a moment, his daughter, wife and two sons all suddenly disappear – victims of the 50% erasure. Hawkeye’s loss is both excessive and insurmountable. He loses everything.
Versions of this continuing loss permeate the movie. Hawkeye retreats into his vengeful violent superhero persona. Thor drinks himself, comically, into oblivion. Captain America runs group counselling sessions helping people to move on.
The differing manifestations of grief are represented in different characters – denial, anger, depression, bargaining, even acceptance. But these are not stages that characters work through. Ultimately all the characters are grief-stricken and unable to move forwards, except for Tony Stark, who has moved on but decides that, in a hastily explained piece of time-travel sleight of hand, he can fix the most of the problems without losing the future he has created for himself.
Nonetheless, the future in which our environmental problems are resolved is infused with melancholy. While Thanos’s rural retreat is a pastoral idyll, the rest of the world is empty, seemingly devoid of life. When Captain America mentions the environmental restoration, he is flippantly dismissed by Black Widow:
You know, if you’re about to tell me to look on the bright side – I’m about to hit you in the head with a peanut butter sandwich.
In traditional superhero stories, the hero(ine) must sacrifice the thing they love most for the betterment of the world. But in Infinity War and Endgame, the heroes sacrifice the betterment of the world to save (or at least reconcile with) the things they love best. Individual interests win out over social or environmental restoration. Rather than securing the future we need, they save the world of the past. With superheroes like this, my sympathies lie with the villains (and not just because of Tom Hiddleston).
So, is Endgame a paean to conservative values, a retreat to an idealised version of the past, a failure to meet the genuine challenges that face the Earth and its ever expanding human population?
Nathaniel Rich, author of Odds Against Tomorrow (2013) once argued: “I don’t think that the novelist necessarily has the responsibility to write about global warming … but I do feel novelists should write about what these things do to the human heart.” This is true of movies too.
What Endgame reveals is that in our hearts we are afraid that the price of environmental salvation is too high, that the losses will be too great, that we will not be able to cope with the scale of the personal sacrifice required.
An insight into the cultural zeitgeist
There is no point in complaining that there are no great climate change movies, or books, with real solutions, or which inspire real action. This is not their purpose. Movies and books don’t help us to overcome our fears, they simply express them. But surely they also reinforce them. Cliched fears about the risks of environmental change, scientists and technology may not be intentionally promoted but they risk promulgating pervasive subconscious biases that both perpetuate and delay vital cultural change.
The real risks of environmental inaction, of course, massively outweigh the risks of any environmental action. But that message does not yet seem to be permeating the popular psyche.
It may well be true, too, that the worst environmental costs will not be borne by the relatively well-off viewers of Avengers movies, but disproportionately by poorer and more vulnerable communities (something that only heightens the irony of fictional East African nation Wakanda’s role in the Avengers franchise).
Effective environmental action does not demand the destruction of half the human population. But it does require the vastly more efficient use and distribution of resources. The sacrifice is not that of the individual, but the vested interests in old-world resources and technology who would prefer not to incur the costs of change. Responding to environmental change does not threaten our comforts, but failing to act will.
Endgame isn’t the endgame: it’s an insight into the cultural zeitgeist. Neither threats nor solutions come from purple aliens, gods or superheroes. They come from us – politicians, scientists, environmentalists, industry and the general public.
Markets, technology and industries can and will adapt rapidly to changing circumstances, in milliseconds, months or even decades. Economies recover, but species do not. The environment takes millennia to adapt and what is lost never comes back. We need to face our fears and find solutions to these problems, rather than just perpetuating the fantasy of regressing into the past.
As Peter Parker says: “You can’t be a friendly neighbourhood Spider-Man, if there’s no neighbourhood.”![]()
Danielle Clode, Senior Research Fellow in Creative Writing, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.